迷走神經消化不良Vagal indigestion
• 慢性狀態,發作慢Chronic condition, slow onset
• 攝取物質無法適當地從瘤胃移動到皺胃,或從皺胃進到幽門Ingesta are not properly transported from the rumen to abomasum or from abomasum to pylorus
• 大量的攝取物質、液體+/-氣體主要蓄積在瘤胃中(也在其他前胃和皺胃中) Large amounts of ingesta, fluid +/- gas accumulate mainly in rumen (also in other forestomachs and abomasum)
• 造成腹部脹大Result is abdominal distension
─ 病因學/致病機轉Vagal indigestion – aetiology/ pathogenesis
ü 未完全瞭解Not fully understood
ü 迷走神經在食道兩側活動,造成前胃和皺胃分佈的神經靜止Vagus nerve runs along both sides of oesophagus and terminates by innervating forestomachs and abomasum
ü 此處神經的功能受損,會引起臨床症狀Impairment in function of this nerve may result in clinical signs
ü 蜂巢胃的移動性發生機能性損傷,以及食道溝的功能障礙(蜂巢胃黏附)是最主要的原因Mechanical impairment of reticular motility and oesophageal groove dysfunction (reticular adhesions) most important cause
ü TPR是主要造成消化不良的原因TRP is responsible for most cases of vagal indigestion
ü 其他原因包括Other causes include:
‧蜂巢胃壁的放線桿菌病Actinobacillosis of reticular wall
‧心臟的纖維乳突狀瘤Fibropapilloma of the cardia
‧腹膜炎(皺胃潰瘍穿孔) Peritonitis (perforating abomasal ulcer)
‧感染或贅瘤Infections or neoplasia
‧橫隔膜破裂、腹膜炎 Ruptured diaphragm, pleurisy
‧肝膿瘍Liver abscess
‧牛隻死後剖檢可能找不出病因No cause may be seen on post mortem
─ 臨床症狀Vagal indigestion – clinical signs
p 瘤胃腫大Enlarged rumen
‧有/無氣泡沫的氣體蓋使背囊擴張而腫大Distended dorsal sac with gas cap ± frothy ingesta
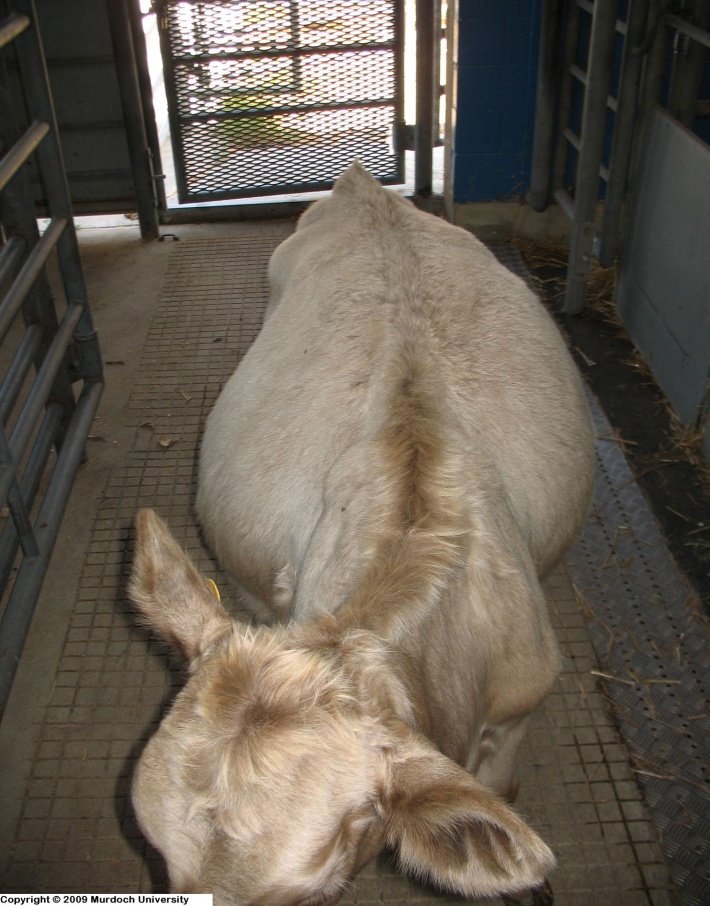
‧腹囊脹大,從後方擠壓使瘤胃呈L形 ─「papple」形Ventral sac then enlarges creating an L shaped rumen from behind –”papple” shape
‧後期病例─直腸檢查顯示右腹囊脹大Advanced cases – rectal exam reveals enlarged right ventral sac
‧間歇性腹部膨脹,在數週 至 數月的時間內會轉成慢性Abdominal distension intermittent but becomes chronic over weeks – months
‧懷孕末期的子宮脹大,能遮蔽住瘤胃脹大的右腹囊Uterine enlargement in late pregnancy may mask distension of right ventral sac of rumen
腫脹的背囊(左側) Enlarged dorsal sac (left side) (Photo: Murdoch University)
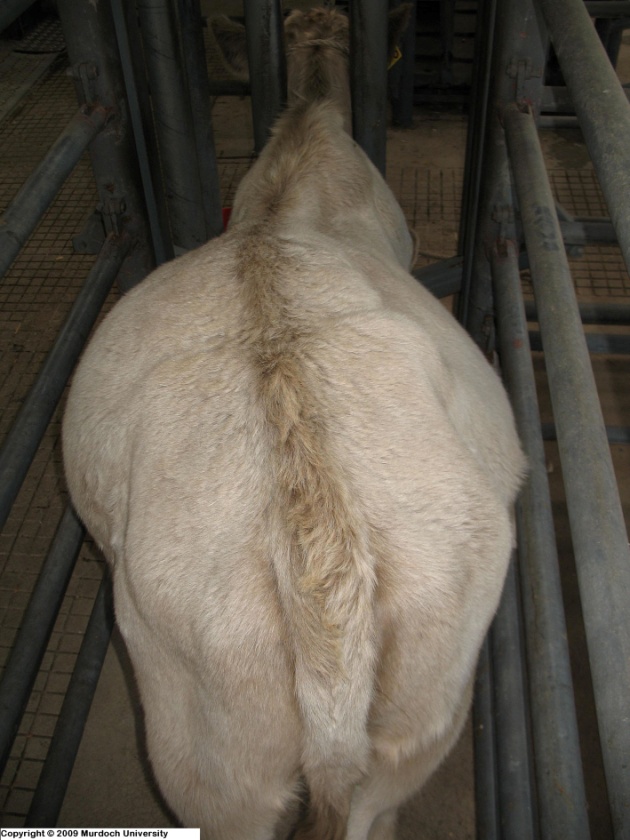
腫脹的腹囊(右側)Enlarged ventral sac (right side) (Photo: Murdoch University)

─ 臨床症狀Vagal indigestion – clinical signs
ü 瘤胃收縮頻率弱 (3~6次/分鐘) Frequent weak rumen contractions (3 – 6/ min)
ü 食慾減退(視腹部腫大程度及排便量而定) ↓ Appetite (varies with amount of abdominal distension and faeces produced)
ü 少量的黏糊便或水便Small amount of pasty or runny faeces
ü 失重Weight loss
ü 產乳量降低↓ milk production
ü 可能出現心跳變慢 (40 bpm) Bradycardia (40bpm) may be present
─ 診斷 Vagal indigestion – diagnosis
ü 無特定的實驗室檢測No specific laboratory tests
ü 嗜中性白血球+/-左移表示炎症反應 Neutrophilia +/- left shift indicates inflammation
ü 血漿蛋白及纖維素原增加↑ plasma protein and fibrinogen
ü 球蛋白增加 = 蜂巢胃膿瘍或肝膿瘍?↑ globulin = reticular or hepatic abscess?
ü 淋巴肉瘤─ 持續性的淋巴球過多症Lymphosarcoma – persistent lymphocytosis
ü 幽門狹窄症─吸收物從皺胃逆流到蜂巢芻胃中,使瘤胃液中氯化物增加Pyloric stenosis - reflux of ingesta from abomasum into reticulorumen increases chloride content of rumen fluid
─ 預後及治療Vagal indigestion – prognosis and treatment
ü 預後差Poor to hopeless prognosis
ü 商業牛 ─ 送去屠宰Commercial cattle – salvage slaughter
ü 有價值的牛隻Valuable animals ─
‧再成水化物Rehydrate
‧考慮進行剖腹探查術以確認主因(左側,瘤胃切開術) Consider exploratory laparotomy to establish primary cause (left side, rumenotomy)
‧長期存活的牛隻以手術治療仍差(只在懷孕末期採用) Long term survival still poor with surgery (salvage procedure for late pregnancy cases)